Printing technology continues to shape the modern manufacturing and packaging industries. From commercial printing to product labeling, the right printing press plays a vital role in ensuring production efficiency, print quality, and brand consistency.
In this guide, we’ll explore the six major types of printing machines — their principles, advantages, and ideal applications — to help you make informed investment decisions for your business.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Choosing the Right Printing Machine Matters
Selecting the right printing equipment is not just a technical choice — it directly impacts cost efficiency, scalability, and customer satisfaction.
Impacts Production Efficiency and Cost
A well-matched high-speed printing machine streamlines production, reduces manual intervention, and cuts operational costs. For large-volume printing, faster setup and automated systems can make a significant difference in output and profit.
Determines Print Quality and Material Compatibility
Different printing presses use varied techniques — toner, inkjet, or flexible plates — each affecting resolution, ink adhesion, and compatibility with materials such as paper, film, foil, or textiles.
Supports Scalability and Product Variety
With growing demand for short-run and personalized printing, digital printing machines allow quick changeovers and flexible design adjustments without compromising color consistency or quality.
The 6 Major Types of Printing Machines
Flexographic (Flexo) Printing Machine
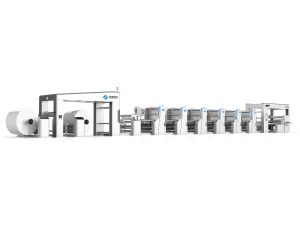
The flexo printing machine is one of the most widely used technologies in packaging and label production. It employs flexible relief plates mounted on rotating cylinders to transfer ink efficiently across various materials.
Applications: Labels, packaging films, corrugated boxes, and folding cartons.
Advantages:
-
Extremely fast and efficient for long production runs
-
Prints on multiple substrates including paper, plastic, and foil
-
Integrates with inline finishing machines for coating, laminating, or embossing
Flexo printing is the backbone of the packaging industry — offering unmatched speed, cost efficiency, and print versatility.

Digital Printing Machine
A digital printing machine transfers images directly from a digital file to the substrate, eliminating the need for traditional plates. It’s ideal for short runs, on-demand jobs, and customized packaging.
How it works: Uses toner or inkjet heads to apply color directly onto paper, film, or board.
Applications: Brochures, marketing materials, product packaging, and personalized labels.
Advantages:
-
Fast setup and minimal prepress requirements
-
Perfect for variable data and short-run production
-
Compatible with automated finishing machines for coating and die-cutting
Inkjet Printing Machine
The inkjet printing machine uses microdroplets of liquid ink to create high-resolution images. Its versatility makes it a top choice for packaging, label printing, and specialty products.
Applications: Labels, flexible films, folding cartons, and signage.
Advantages:
-
Exceptional print clarity and color accuracy
-
Works with various materials, including paper, foil, and synthetics
-
Low ink waste and quick color changeovers
Inkjet systems are a cornerstone of modern digital printing machines, bridging precision and flexibility for today’s packaging and labeling needs.
Laser Printing Machine
A laser printing machine uses heat and pressure to fuse toner powder onto a substrate, enabling high-speed, durable, and consistent prints.
Applications: Commercial documents, barcode labels, product inserts, and office printing.
Advantages:
-
High speed with crisp, durable results
-
Reliable performance and low maintenance
-
Ideal for mass document or variable data production
Laser systems are widely used in both office environments and industrial settings where efficiency and accuracy are critical.
Offset Printing Machine
An offset printing press uses metal plates and rubber blankets to transfer ink onto paper or board. It remains the industry standard for commercial and publication printing.
Applications: Magazines, catalogs, books, and marketing materials.
Advantages:
-
Excellent color consistency and print detail
-
Highly cost-effective for large-volume printing
-
Compatible with advanced finishing machines for binding and coating
Offset printing continues to dominate high-quality, high-volume printing thanks to its balance of efficiency and precision.
Screen Printing Machine
Screen printing (also known as silkscreen printing) forces ink through a mesh stencil onto a material surface. It’s especially popular for decorative and promotional applications.
Applications: Apparel, signage, promotional items, and product packaging.
Advantages:
-
Produces rich, vibrant colors with strong opacity
-
Works on diverse materials including fabric, glass, plastic, and metal
-
Durable prints suitable for outdoor and heavy-use environments
Screen printing remains a vital part of the industrial printing press landscape due to its flexibility, durability, and creative potential.
How to Choose the Right Printing Machine
Choosing the right printing technology depends on your production goals, material types, and operational budget.
Match machine type to production volume and material
-
Flexo printing machines excel in high-volume packaging runs.
-
Digital and inkjet machines suit short runs and custom projects.
Consider quality requirements and finishing options
For coatings, lamination, or embossing, ensure your setup includes compatible finishing machines or inline finishing systems.
Evaluate ROI and maintenance support
Assess long-term costs, including inks, energy use, and spare parts, to understand total return on investment.
Plan for scalability
Invest in modular or upgradeable systems to accommodate future business growth and diversification.
FAQs
Which printing machine works best for packaging?
Flexo and gravure printing machines are preferred. Flexo provides speed and versatility; gravure delivers premium image depth. Hybrid systems combine digital and flexo for short-run packaging.
How to choose the right printing press?
Base your choice on volume, substrate, finishing, and ROI. Flexo suits mass production; digital fits short runs. Ensure compatibility with finishing and automation systems.
How can I reduce waste and material costs in my print production?
Implement printing automation, precise ink management, and inline finishing to minimize offcuts and misprints.
What factors affect print quality consistency across multiple machines?
Ink type, substrate, machine calibration, and finishing integration are critical. Automation and inline quality control systems improve reproducibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the main printing technologies — from flexo and digital to inkjet, offset, and screen printing — helps businesses make smarter production decisions.
-
Flexo printing machines dominate packaging for their speed and versatility.
-
Digital printing machines lead in customization and short-run agility.
-
Offset and screen presses continue to provide high-quality results for mass production.
Selecting the right printing press ensures you stay competitive, efficient, and ready for market changes.
Not sure which machine suits your production needs? Contact our specialists to discuss your workflow goals and find the ideal solution for your business.