In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, choosing the right machinery for material processing is critical. Two of the most common types of equipment used across various industries are the slitting machine and the cutting machine. Though they may seem similar at first glance, they serve entirely different functions and are used in distinct applications.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- What is a slitting machine?
- How slitting machinery differs from cutting equipment
- How to choose the right tool for your production line
Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
Toggle1.What is a Slitting Machine?
Definition
A slitting machine is a type of slitting equipment used to convert large rolls of material into narrower rolls by slicing them lengthwise. This process is commonly known as web slitting, and it’s essential in industries that work with continuous rolls of materials like plastic film, aluminum foil, paper, and metal sheets.
Working Principle
The machine unwinds a parent roll, passes it through rotary slitting blades, and rewinds the slit material into smaller rolls.
【Slitting Machine: Parts, Function, Parameters and Working Principle】
Common Applications
Used extensively in:
- Flexible packaging
- Electrical insulation materials
- Adhesive tapes
- Metallized films
- Paper and cardboard rolls
Types of Slitting Methods
- Roll-to-roll slitting machines
- Razor slitting
- Shear slitting
- Crush (score) slitting
Pro Tip: High-quality slitting machinery includes automatic tension control, high-speed blade adjustment, and precision alignment systems.
2.What is a Cutting Machine?
A cutting machine is used to divide materials into specific lengths or shapes. Unlike a slitting machine which slices material along its length, a cutting machine typically cuts across the material’s width or into defined patterns.
Working Principle
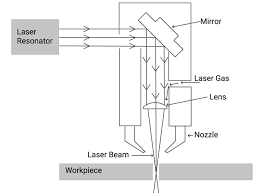
The material (sheet or roll) is placed into the cutting system where blades or lasers slice it transversely (crosswise) or into specific forms.
【The details working principle of laser cutting machine】
Common Applications
- Label and sticker production
- Garment and textile manufacturing
- Sheet metal cutting
- Leather or rubber processing
Common Cutting Technologies
- Guillotine cutting
- Die-cutting
- Laser cutting
- CNC-controlled cutters
3.Key Differences Between Slitting and Cutting Machines
| Aspect | Slitting Machine | Cutting Machine |
| Purpose | Reduce roll width on longitudinal axis | Cut to shape/length in crossdirection or custom profiles |
| Direction of cutting | Lengthwise along roll | Crosswise or multiaxis |
| End products | Narrow rolls (“daughter rolls”) ready for further rollfeed use | Sheets, custom shapes, parts |
| Blade type | Rotary knives (razor, shear, crush) | Guillotine blades, dies, lasers, CNC tools |
| Material type | Flexible rolls: film, paper, fabric, foil, metal coils | Broad: rigid or sheet materials—metal, plastic, wood, composites |
| Rewinding | Yes – always rewinds strips into rolls | Typically no rewinding—finished parts removed after cut |
| Automation & speed | Highly automated, running at high speeds (up to several km/min) | Varies—lasers & CNC slower, diecutters faster but less continuous |
| Typical precision | Tolerance within mm, optimized for width | High precision—often thousandths of an inch, depending on method |

Vs
【Industrial guillotines – cross-cutting machines】
4.How to Choose Between Slitting and Cutting Machines
Here are five key factors to consider when deciding between slitting machinery and cutting systems:
| Criteria | Best with Slitting Machine | Best with Cutting Machine |
| Material Format | Large rolls requiring width reduction | Sheets or rolls needing short cuts or shapes |
| Desired Output | Narrow reels/coils | Sheets, die-cut parts, or labels |
| Industry Needs | Printing, tape, metal coil processing | Textile, signage, packaging |
| Cutting Complexity | Straight slits only | Variable patterns, curves, and perforations |
| Speed & Volume | High-speed roll-to-roll slitting | Medium to high-volume cut jobs |
5.Innovations in Slitting and Cutting Technologies
Manufacturers are integrating intelligent systems into slitting equipment and cutting machines to improve:
- Precision and speed
- Remote diagnostics
- Energy efficiency
- Data logging for quality control
Examples:
- Slitting machines with servo-driven tension control and web guide systems
- Cutting machines using laser guidance and IoT-based maintenance alerts
Closing Remarks
Both slitting machines and cutting machines play crucial roles in modern production lines, but their functions, mechanics, and applications are distinctly different.
- Use slitting machinery when processing wide rolls into narrow, precise widths.
- Choose cutting machines for shape- or length-based conversions of sheet or roll material.
By understanding what is slitting machine and how it compares to traditional cutting systems, businesses can make more informed decisions about optimizing their manufacturing operations.
Need help choosing the right slitting equipment?
Let us know your material type, width, and volume — we’ll recommend the ideal solution tailored to your production needs.